- Switch

- Router
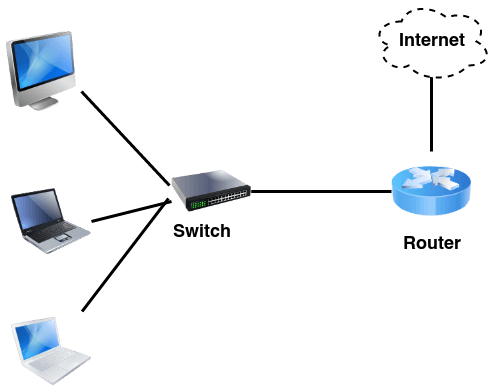
Routing
IP routing is the process of sending packets from a host on one network to another host on a different remote network. This process is usually done by routers. Routers examine the destination IP address of a packet , determine the next-hop address, and forward the packet. Routers use routing tables to determine a next hop address to which the packet should be forwarded.
In other word, “Routing is the process of selecting a path for traffic in a network or between or across multiple networks.”
Consider the following example of IP routing:
Host A wants to communicate with host B, but host B is on another network. Host A is configured to send all packets destined for remote networks to router R1. Router R1 receives the packets, examines the destination IP address and forwards the packet to the outgoing interface associated with the destination network.
Types of Routing
There are three types of routing.
- Static Routing
- Dynamic Routing
- Default Routing

Well done!!
ReplyDelete