OSI MODEL
___________________________________________________________________________
- OSI Model
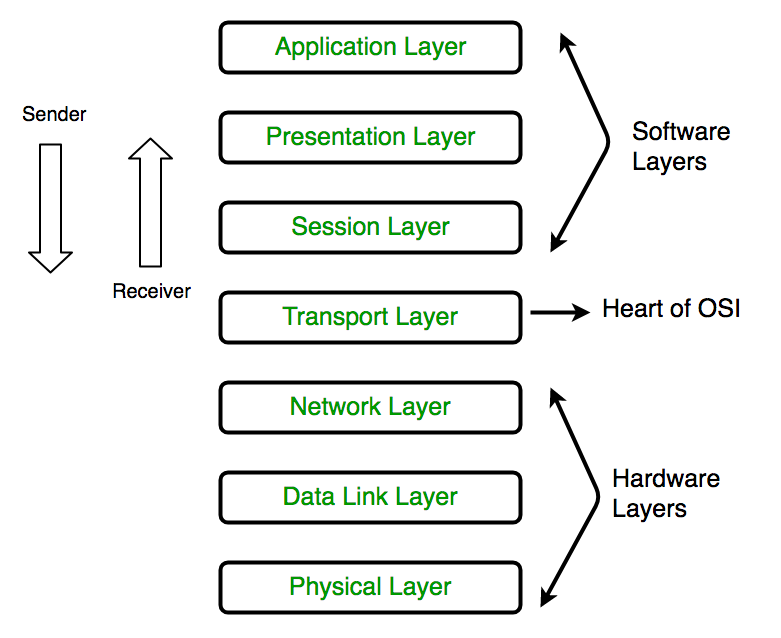
- Physical Layer (Layer 1)
The functions of the physical layer are:
- Dividing Data into Bits steam.
- Encoding Bits steam into signals.
- Topology.
- Transmission media type / speed.
- Device
- Cable,
- Connectors,
- Modern,
- Repeater,
- HUB.
Data Link Layer (Layer 2)
The data link layer is responsible for the node to node delivery of the message. The main function of this layer is to make sure data transfer is error free from one node to another, over the physical layer. When a packet arrives in a network, it is the responsibility of DLL to transmit to the Host using its MAC address.
Data Link Layer is divided into two sub layers:
- Logical Link Control (LLC)
- Media Access Control (MAC)
1) Framing: It provides a way for a sender to transmit a set of bits that are meaningful to the receiver.
2) Physical addressing: After creating frames, Data link layer adds physical addresses (MAC address) of sender and/or receiver in the header of each frame.
3) Error control: Data link layer provides the mechanism of error control in which it detects and re-transmits damaged or lost frames.
4) Flow Control: The data rate must be constant on both sides else the data may get corrupted thus, flow control coordinates that amount of data that can be sent before receiving acknowledgement.
5) Access control: When a single communication channel is shared by multiple devices, MAC sub-layer of data link layer helps to determine which device has control over the channel at a given time.
Devices:
NIC (LAN Card), Bridge, Switch, Access point.
NIC (LAN Card), Bridge, Switch, Access point.
Protocols:
HDLC, PPP, Frame Relay.
- Network Layer (Layer 3)
The functions of the Network layer are:
1) Routing: The network layer protocols determine which route is suitable from source to destination. This function of network layer is known as routing.
2) Logical Addressing: In order to identify each device on inter-network uniquely, network layer defines an addressing scheme. The sender & receiver’s IP address are placed in the header by network layer.
* Segment in Network layer is referred as Packet.
Devices
Router, L3 Switch, Brouter (Bridge + Router) - Transport Layer (Layer 4)
The functions of the transport layer are:
1) Segmentation and Reassembly: This layer accepts the message from the (session) layer breaks the message into smaller units. Each of the segments produced has a header associated with it. The transport layer at the destination station reassembles the message.
2) Service Point Addressing: In order to deliver the message to correct process, transport layer header includes a type of address called service point address or port address. Thus by specifying this address, transport layer makes sure that the message is delivered to the correct process.
Protocol
TCP (Transmission control Protocol).
UDP (User Datagram Protocol).
- Session Layer (Layer 5)
The functions of the session layer are:
1) Session establishment, maintenance and termination: The layer allows the two processes to establish, use and terminate a connection.
2) Synchronization: This layer allows a process to add checkpoints which are considered as synchronization points into the data. These synchronization point help to identify the error so that the data is re-synchronized properly, and ends of the massage not cut prematurely and data loss is avoided.
3) Dialog Controller: The session layer allows two systems to start communication with each other in half-duplex or full-duplex.
- Presentation Layer (Layer 6)
The functions of the presentation layer are:
1) Translation: For example, ASCII to EBCDIC.
2) Encryption/ Decryption: Data encryption translates the data into another form or code. The encrypted data is known as the cipher text and the decrypted data is known as plain text. A key value is used for encrypting as well as decrypting data.
3) Compression: Reduces the number of bits that need to be transmitted on the network.
- Application Layer (Layer 7)
Ex: Application – Browsers, Skype Messenger etc.
**Application Layer is also called as Desktop Layer.
The functions of the Application layer are:
1. Network Virtual Terminal
2. FTAM-File transfer access and management
3. Mail Services 4. Directory Services
Comments
Post a Comment