COMPUTER NETWORK
_____________________________________________________________________________
A network is a group of two or more computer systems, which are linked together. It also consists of a collection of computers, printer, scanner and other devices that are connected together.
Types of Computer Network
- LAN
- CAN
- MAN
- WAN
- PAN
LAN stands for Local Area Network. It is used to network computers within a limited area like office, school by using the network media.
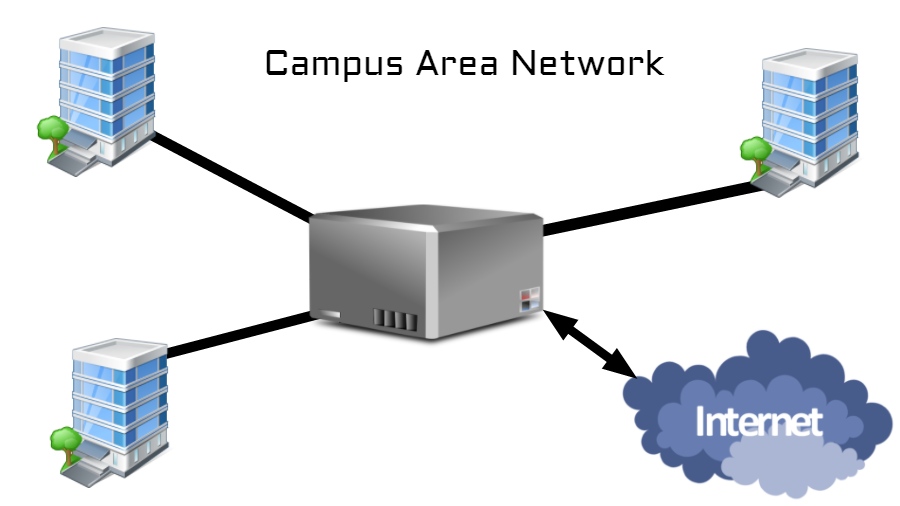
Campus area network is an interconnection of local area network (LAN) within a limited geographical area. Campus network can be additional to the set of wireless connections, connect several buildings to the same network, but it’s not the same thing. A CAN is smaller than a wide area network. Example: Corporate office campus, university etc. have interconnected administrative buildings.
MAN means Metropolitan area network, which optimized for a larger geographical area than a LAN, ranging from several blocks of buildings to entire city.
WAN is Wide Area Network that is a network connection of wide area such as the world.
PAN is a Personal Area Network which is referred to the interconnection of information computers, mobile phones.
- Network Transmission Media
There are two types of transmission media is used in Networking.
- Wired (cable)
- Wireless (Air)
There are three types of Wired Transmission Media.
- Coaxial cable
- Twisted pair cable
- Fiber optic cable
It has an outer plastic covering containing two parallel conductors each having a separate insulated protection cover. Coaxial cable transmits information in two modes: Baseband mode (dedicated cable bandwidth) and Broadband mode(cable bandwidth is split into separate ranges).
Cable TVs and analog television networks widely use Coaxial cables.
Twisted pair cables have been around for a long time. They were mainly invented for voice transmissions. Twisted pair is a widely used medium in networking because it's lighter, cheaper, more flexible, easy to install, and provides greater speeds than coaxial cables.
There are two types of twisted pair cables: the unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and the shielded twisted pair (STP).
Fiber optic is a cable that holds the optical fibers coated in plastic that are used to send the data by pulses of light. The plastic coating protects the optical fibers from heat, cold, electromagnetic interference from other types of wiring. Fiber optics provide faster data transmission than copper wires.

There are many types of networking devices:
- Hub.
- Switch
- Router
- Bridge
- Gateway
- Modem
- Repeater
- Access Point
Hubs connect multiple computer networking devices together. A hub also acts as a repeater in that it amplifies signals that deteriorate after traveling long distances over connecting cables. A hub is the simplest in the family of network connecting devices because it connects LAN components with identical protocols.
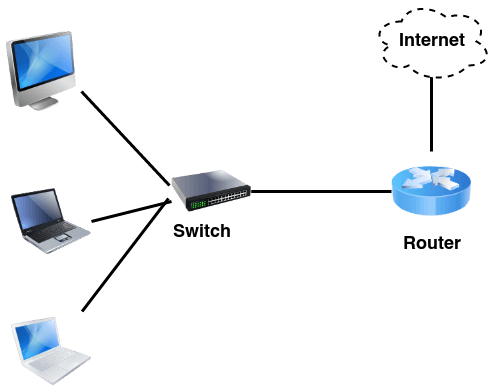
Switches generally have a more intelligent role than hubs. A switch is a multiport device that improves network efficiency. The switch maintains limited routing information about nodes in the internal network, and it allows connections to systems like hubs or routers. Strands of LANs are usually connected using switches. Generally, switches can read the hardware addresses of incoming packets to transmit them to the appropriate destination.

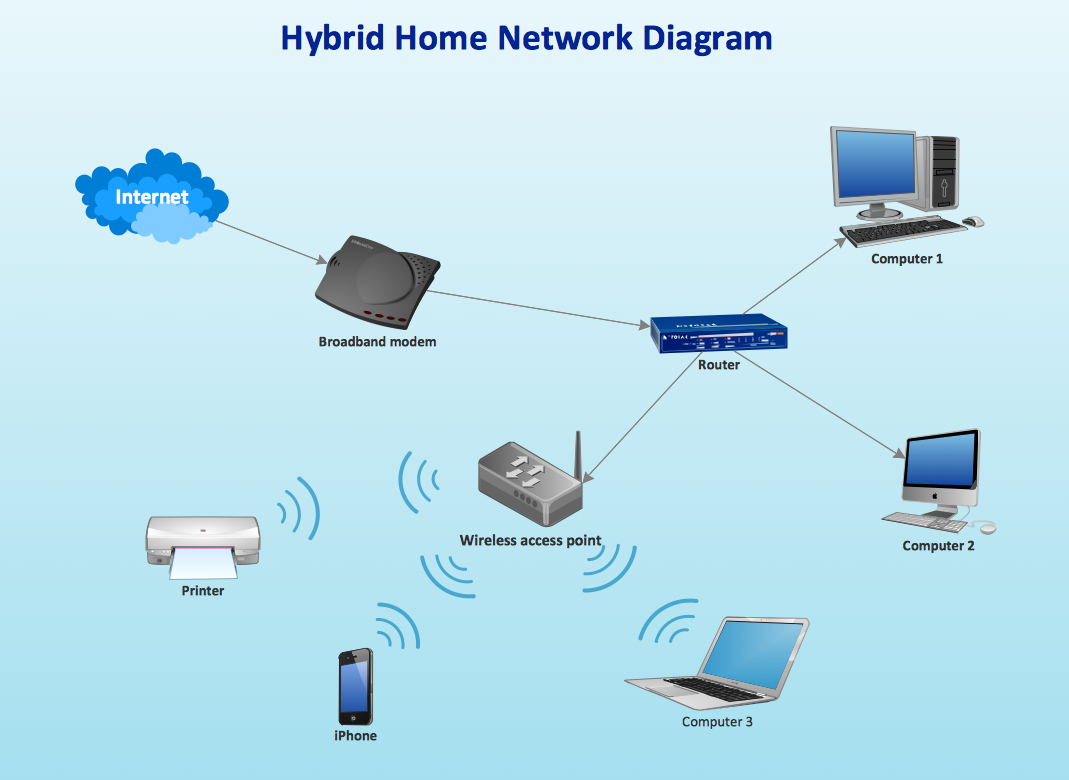
Routers help transmit packets to their destinations by charting a path through the sea of interconnected networking devices using different network topologies. Routers are intelligent devices, and they store information about the networks they’re connected to. Most routers can be configured to operate as packet-filtering firewalls and use access control lists (ACLs). Routers, in conjunction with a channel service unit/data service unit (CSU/DSU), are also used to translate from LAN framing to WAN framing. This is needed because LANs and WANs use different network protocols. Such routers are known as border routers. They serve as the outside connection of a LAN to a WAN, and they operate at the border of your network.
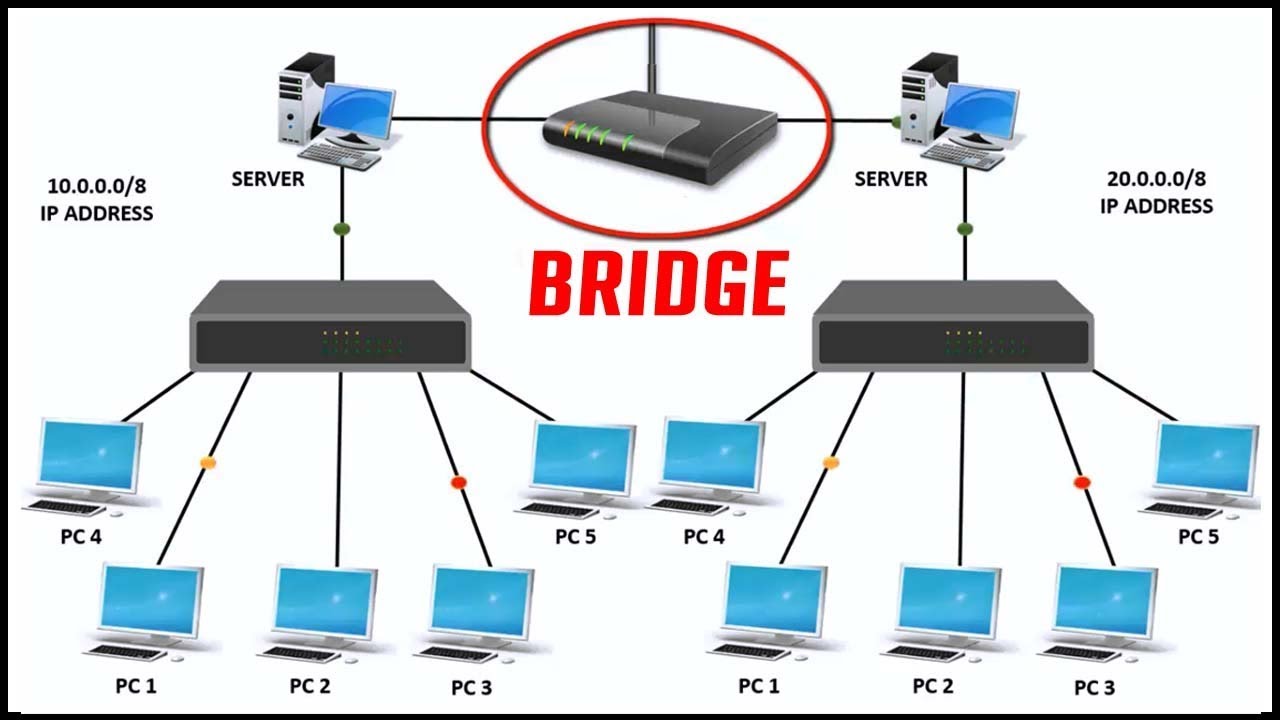
Bridges are used to connect two or more hosts or network segments together. The basic role of bridges in network architecture is storing and forwarding frames between the different segments that the bridge connects. They use hardware Media Access Control (MAC) addresses for transferring frames. By looking at the MAC address of the devices connected to each segment, bridges can forward the data or block it from crossing. Bridges can also be used to connect two physical LANs into a larger logical LAN.
Gateways normally work at the Transport and Session layers of the OSI model. At the Transport layer and above, there are numerous protocols and standards from different vendors; gateways are used to deal with them. Gateways provide translation between networking technologies such as Open System Interconnection (OSI) and Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP). Because of this, gateways connect two or more autonomous networks, each with its own routing algorithms, protocols, topology, domain name service, and network administration procedures and policies.

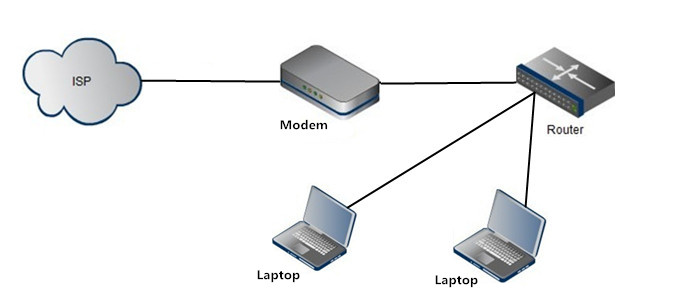
Modems (modulators-demodulators) are used to transmit digital signals over analog telephone lines. Thus, digital signals are converted by the modem into analog signals of different frequencies and transmitted to a modem at the receiving location. The receiving modem performs the reverse transformation and provides a digital output to a device connected to a modem, usually a computer. The digital data is usually transferred to or from the modem over a serial line through an industry standard interface, RS-232. Many telephone companies offer DSL services, and many cable operators use modems as end terminals for identification and recognition of home and personal users. Modems work on both the Physical and Data Link layers.
A repeater is an electronic device that amplifies the signal it receives. You can think of repeater as a device which receives a signal and retransmits it at a higher level or higher power so that the signal can cover longer distances, more than 100 meters for standard LAN cables. Repeaters work on the Physical layer.
While an access point (AP) can technically involve either a wired or wireless connection, it commonly means a wireless device. An AP works at the second OSI layer, the Data Link layer, and it can operate either as a bridge connecting a standard wired network to wireless devices or as a router passing data transmissions from one access point to another.
- Connector used in Transmission Media
There are three type of connector used in Transmission Media:
- Coaxial – BNC connector
- Twisted pair – RJ45 or RJ11
- Fiber Optics – SC, ST, FC, LP
- Twisted pair – RJ45 or RJ11
Cable Stripper & Crimping Tool: It is a tool used to strip the outer coating of cable.
- Scissor: Diagonal Cutter is used to cut the cable or trim wire end.
- Tester: Tester checked wire connection right or wrong.

- Fiber Optics – FC, ST, LC, SC
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Sample-network-diagram-52ae9f4ac5a94c6fb090a315f1b7c3d3.jpg)


















Comments
Post a Comment