BASIC DISK & DYNAMIC DISK & FILE FORMAT
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- Basic Disk
"Basic disk uses partitions to manage data, and one partition cannot share and split data with other partitions." (the late versions of Windows OS like Windows 7, Windows 8 and Windows 10 also call partitions volumes).
On a basic disk, we can create 2 styles of partitions, namely MBR style partition and GPT style partition. To create MBR style partitions, we need to initialize the hard disk to MBR (master boot record). To create GPT style partitions, we should initialize the disk to GPT (GUID partition table).
MBR and GPT partition style
On MBR disks, partitions are called primary partition, extended partition, or logical partition while all partitions on GPT disk are called GPT partitions which function like primary partitions. An MBR based basic disk can have four primary partitions or three primary plus one extended partition, but the extended partition can contain an unlimited number of logical drives. And a GPT based hard disk can hold up to 128 partitions.
We can extend a primary partition by adding contiguous unallocated space on the same disk or extend a logical drive by adding free space contained in extended partition, but these partitions should be formatted with NTFS file system. Otherwise, Extend Volume feature is grayed out.
- Dynamic Disk
Dynamic disk uses dynamic volumes to manage data. It is a separate form of volume management that allows one volume to have non contiguous extents on one or more physical disks. Dynamic disks use a database to track information about all volumes on the disk as well as information about other dynamic disks, and the location of the database is determined by partition style of the disk.
On MBR partitions, the database is contained in the last 1 megabyte (MB) of the disk while database on GPT partitions is located in a 1 MB reserved partition. In addition, each dynamic disk in a computer saves a copy of the database, so that Windows can repair a damaged database by using the database on other dynamic disks.
On a dynamic disk, we can create 5 types of dynamic volumes to enhance computer performance, including simple volume, mirrored volume, striped volume, spanned volume, and RAID-5 volume.
- Simple volume functions like primary partitions on basic disk;
- Mirrored volume provides fault tolerance by creating a copy of data contained in this volume;
- Striped volume improves disk input/output performance by distributing I/O requests across disks; Spanned volume combines spaces on 2 hard disks at least to a dynamic volume;
- RAID-5 volume stripes data and parity across three or more disks.
For more information about these volumes, please see Dynamic Disk.
In Windows snap-in Disk Management utility, we are only allowed to extend simple volumes and spanned volumes except for the system and boot one; or we can extend a mirrored volume after breaking the mirror. However, with a third party partitioning program, we can extend any types of dynamic volumes.
- Relationship between Basic Disk and Dynamic Disk
Although basic disk and dynamic disk are 2 types of hard disk configurations, they are not completely irrelevant. Actually, we can convert a basic disk to dynamic disk or turn a dynamic disk to basic disk without data loss when there is a need.
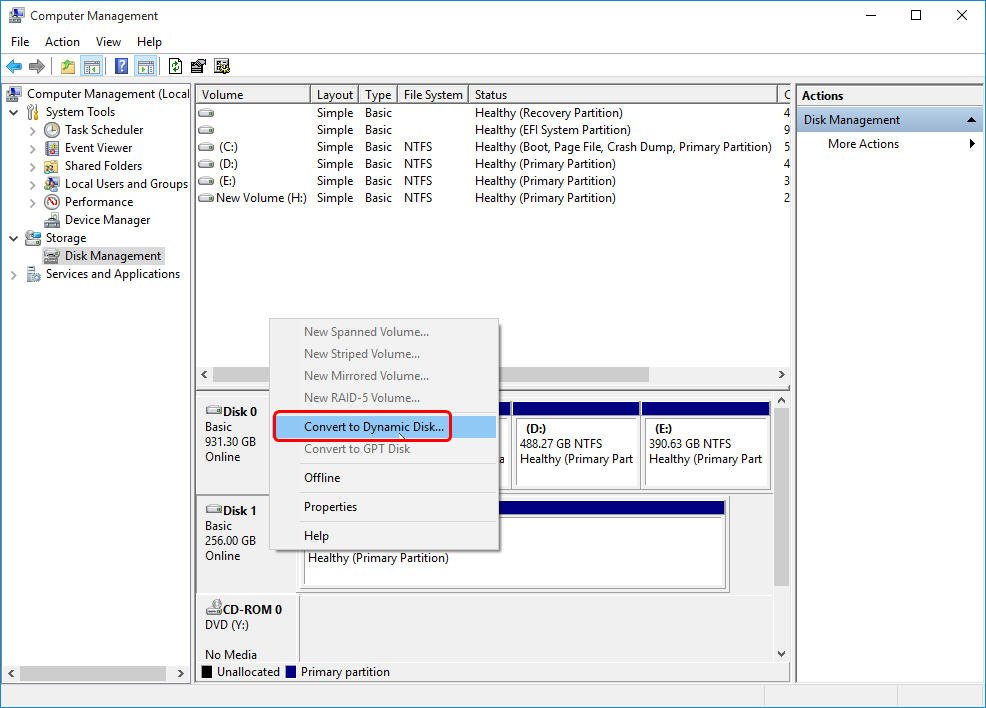
- Configuration steps of converting basic disk to dynamic disk:
Right click the basic disk -> choose "Convert to Dynamic Disk" from the popup menu
-> click "OK" -> tap "Convert" to get the window below:
-> click "OK" -> tap "Convert" to get the window below:

- File System
Three type of File System.

Comments
Post a Comment